Credit Card Fraud Detection using Gradient Boosting and Deep Neural Networks.
Adam Rehman
This project explores the detection of financial fraud in credit card transactions using machine learning techniques. The code and experiments in this repository leverage Kaggle’s Credit Card Fraud Dataset to build and evaluate a fraud detection model. The full source code and details are available in the GitHub repository.
Overview
Data
- The dataset contains transactions labeled as either fraudulent or legitimate.
- It exhibits a strong class imbalance: legitimate transactions vastly outnumber fraudulent ones.
Modeling
- The primary model is an XGBoost (Gradient Boosted Decision Trees) classifier.
- Key configuration parameters include:
max_depth: Controls tree depth to prevent overfitting.learning_rate: Set low for better convergence.n_estimators: High value with early stopping.gamma,alpha,lambda: Regularization terms.scale_pos_weight: Adjusted to address class imbalance.
- A validation set is used to monitor performance, with early stopping or threshold tuning applied.
Here’s a snippet of the model training code:
import xgboost as xgb
# Train the model
params = {
'objective': 'binary:logistic',
'tree_method': 'hist',
'device': 'cpu',
'learning_rate': 0.05,
'max_depth': 10,
'n_estimators': 50000,
'gamma': 10,
'lambda': 10,
'alpha': 1,
'scale_pos_weight': class_imbalance,
'eval_metric': 'auc'
}
model = xgb.XGBClassifier(**params)
model.fit(X_train, y_train, eval_set=[(X_val, y_val)], verbose=False)
model.save_model('xgboost_model.json')
After training, the model is saved as xgboost_model.json for future use. This setup ensures robust performance on the imbalanced dataset. Evaluation Metrics
Precision and Recall are calculated, leading to the F1 Score (harmonic mean).
Fβ Score (e.g., β=10) is computed to prioritize Recall when missing fraud is costly.
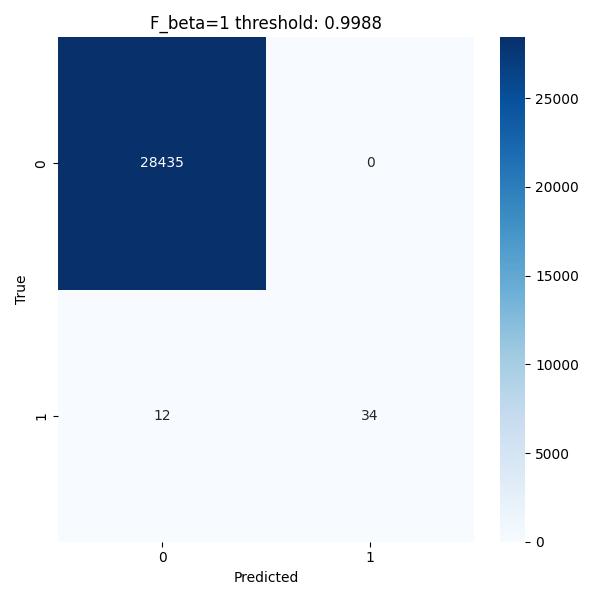
Thresholds are selected to maximize either F1 or Fβ, followed by confusion matrix comparisons.
Threshold Tuning
Default threshold for binary classifiers is 0.5.
Due to imbalance, the threshold is tuned using the Precision-Recall curve to maximize a chosen F-measure.
Confusion Matrices
Side-by-side confusion matrices are plotted for F1-optimized vs. Fβ-optimized thresholds.
This visualizes trade-offs between false positives and false negatives.